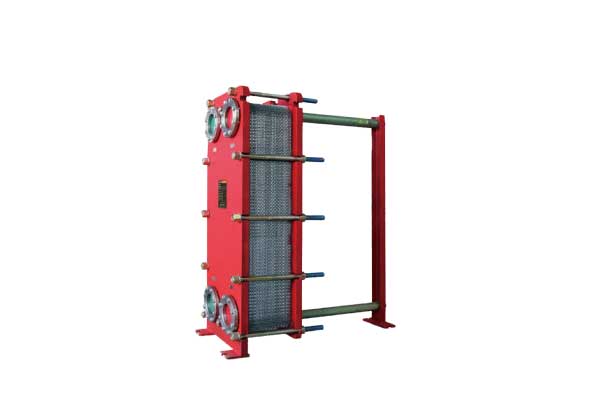
The plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that is formed by pressing thin metal plates into heat exchange plates with certain corrugated points, stacking them, and assembling them using frame plates and clamping bolts. The working principle of the plate heat exchanger is also very simple and easy to understand. The working fluid flows through the narrow and tortuous channel formed between two plates, while the hot and cold fluids flow through the channel plate between the plates for cold and heat exchange. Compared to other types of heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers have many outstanding advantages, such as high heat exchange efficiency, small heat loss, compact structure, small footprint, long service life, and wide application range. It is precisely because the plate heat exchanger has so many advantages that it can win the recognition of users and quickly promote and popularize in the market.
The plate heat exchanger operates on the principle of counter-current flow, where the two fluids flow in opposite directions to each other. This maximizes the temperature difference between the two fluids, resulting in a higher heat transfer rate. The corrugations on the plates create turbulence in the flow, which further enhances the heat transfer coefficient.
The plate heat exchanger is widely used in various industries, such as HVAC, chemical processing, power generation, and food and beverage processing. It has many advantages over traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers, such as higher heat transfer efficiency, compact size, and lower maintenance requirements.
The plate heat exchanger is also easy to clean and maintain. It can be disassembled and cleaned by removing the bolts that hold the frame together. The gaskets can also be easily replaced if they become worn or damaged.
Overall, the plate heat exchanger is a versatile and efficient heat transfer device that is suitable for a wide range of applications. Its compact size and ease of maintenance make it a popular choice for many industries.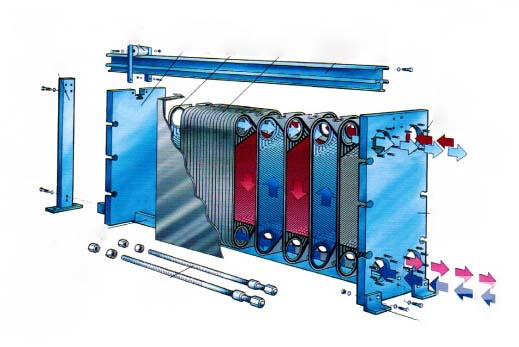
Working Principle:
The plate heat exchanger is a new type of high-efficiency heat exchanger composed of stacked metal plates with a certain corrugated shape. The structure includes gaskets, compression plates (movable end plates, fixed end plates), and frames (upper and lower guide rods, front pillars), etc. The plates are sealed and guided by sealing gaskets, which separate the cold/hot fluid channels. The cold/hot heat exchange medium flows through their respective channels and exchanges heat with the separated plates to reach the temperature required by the user.
There are openings at the four corners of each plate. After being assembled into a plate bundle, the fluid distribution pipes and collection pipes are formed. After the heat exchange of the cold/hot medium, they are recycled from their respective collection pipes.
A stack of plates is formed to create a plate pack with a channel pattern. End base plates with connecting pipes are placed at both ends. The entire device is vacuum-brazed. The two media flow respectively through adjacent channels. The sheets between adjacent channels are corrugated to enhance heat exchange between the two media. In a brazed plate heat exchanger for refrigeration, there is always one more water channel than refrigerant channel.
Structure:
The plate heat exchanger is mainly divided into two types: frame type (detachable type) and brazed type, with plate forms mainly including herringbone corrugated plates, horizontal flat corrugated plates, and tumor-shaped plates.
The main structure of the heat exchanger includes:
-
Plate heat exchanger plates and plate heat exchanger gaskets
-
Fixed pressure plate
-
Movable compression plate
-
Clamping bolts
-
Upper guide rod
-
Lower guide rod
-
Rear column







